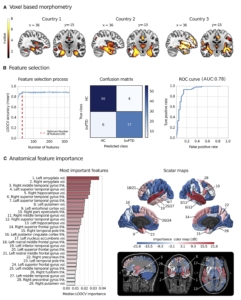
Robust automated computational approach for classifying frontotemporal neurodegeneration: Multimodal/multicenter neuroimaging
Alzheimer’s and Dementia
Donnelly-Kehoe, P., Pascariello, G., García, A. M., Hodges, J., Miller, B., Rosen, H. […] Ibánez, A. & Sedeño, l. (2019). Robust automated computational approach for classifying frontotemporal neurodegeneration: Multimodal/multicenter neuroimaging. Alzheimer’s and Dementia 11, 588-598. Online: http://bit.ly/33uHhBS.
En este reporte multicéntrico de tres centros diferentes implementamos un enfoque computacional para identificar pacientes con demencia frontotemporal. Usando machine learning, combinamos datos cerebrales estructurales y de conectividad cerebral, obteniendo una alta precisión de clasificación (91%) en todos los centros. Este procedimiento permite comparar datos de pacientes de diferentes centros y realizar análisis de forma totalmente automática.
Para leer el artículo completo hacé click AQUÍ
Robust automated computational approach for classifying frontotemporal neurodegeneration: Multimodal/multicenter neuroimaging
Alzheimer’s and Dementia
Donnelly-Kehoe, P., Pascariello, G., García, A. M., Hodges, J., Miller, B., Rosen, H. […] Ibánez, A. & Sedeño, l. (2019). Robust automated computational approach for classifying frontotemporal neurodegeneration: Multimodal/multicenter neuroimaging. Alzheimer’s and Dementia 11, 588-598. Online: http://bit.ly/33uHhBS.
Timely diagnosis of behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia (bvFTD) remains challenging because it depends on clinical expertise and potentially ambiguous diagnostic guidelines. Recent recommendations highlight the role of multimodal neuroimaging and machine learning methods as complementary tools to address this problem.