Rekindling action language: A neuromodulatory study on Parkinson’s disease patients
Suárez-García, D., Birba, A., Zimerman, M., Diazgranados, J., Lopes da Cunha, P., Ibáñez, A., Grisales-Cárdenas, J., Cardona, J. & García, A. M. (2021). Rekindling action language: A neuromodulatory study on Parkinson’s disease patients. Brain Sciences 11(7), 887.
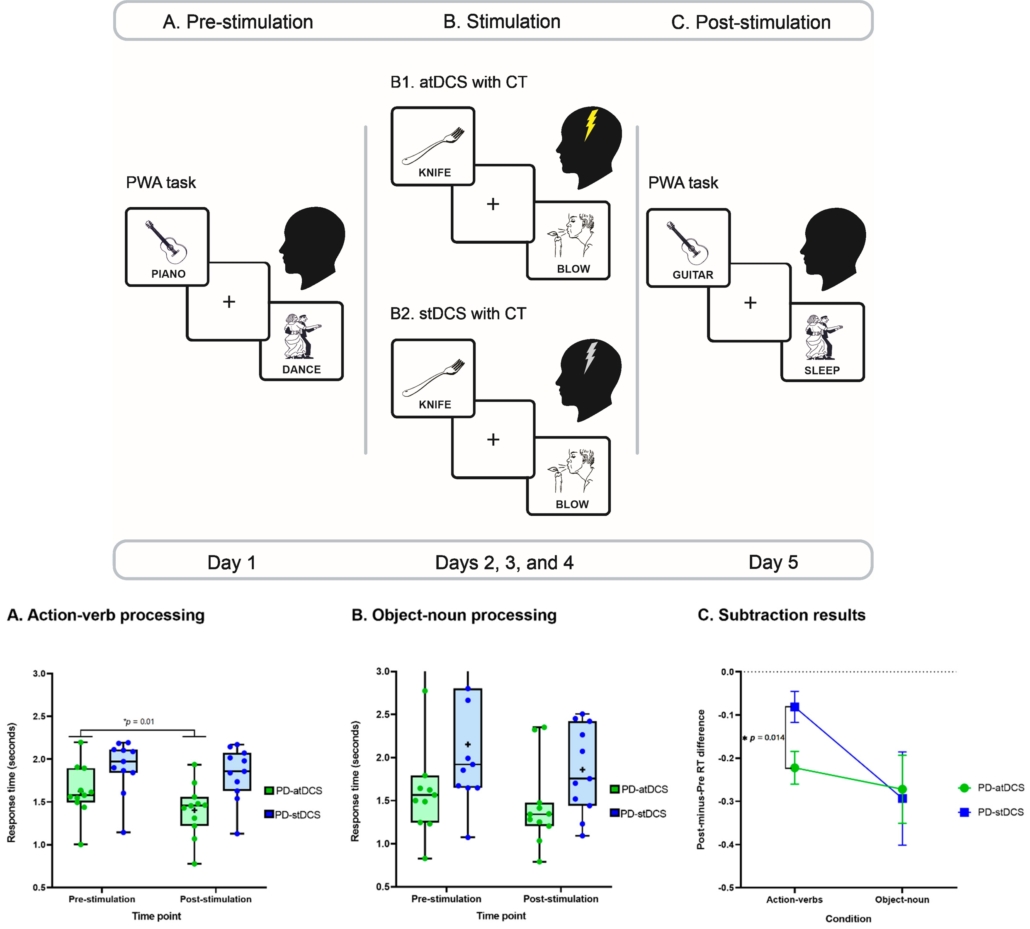
Las personas con enfermedad de Parkinson presentan déficits en la comprensión de acciones corporales. En este estudio, mostramos que la estimulación no invasiva de la corteza motora primaria, sumada a un entrenamiento cognitivo, mejora selectivamente el procesamiento de conceptos de acción en dicha población. Estos efectos se observaron independientemente de las habilidades cognitivas, ejecutivas y motoras de los pacientes. Dichos resultados abren nuevos caminos traslacionales en el campo de la cognición corporizada.
Para acceder al artículo hacé click aquí.
Rekindling action language: A neuromodulatory study on Parkinson’s disease patients
Suárez-García, D., Birba, A., Zimerman, M., Diazgranados, J., Lopes da Cunha, P., Ibáñez, A., Grisales-Cárdenas, J., Cardona, J. & García, A. M. (2021). Rekindling action language: A neuromodulatory study on Parkinson’s disease patients. Brain Sciences 11(7), 887.
To access the paper, please click here.