Interoception primes emotional processing: Multimodal evidence from neurodegeneration
Salamone, P., Legaz, A., Sedeño, L., Moguilner, S., Fraile-Vazquez, M., Gonzalez Campo, C., Fittipaldi, S., Yoris, A., Miranda, M., Birba, A., Galiani, A., Abrevaya, S., Neely, A., Martorell Caro, M., Alifano, F., Villagra, R., Anunziata, F., Okada de Oliveira, M., Pautassi, R., Slachevsky, A., Serrano, C., García, A. M. & Ibañez, A. (2021). Interoception primes emotional processing: Multimodal evidence from neurodegeneration. Journal of Neuroscience 41(19), 4276-4292.
En este trabajo mostramos que los procesos interoceptivos facilitan el reconocimiento de emociones y que dicha interacción se ve alterada en múltiples niveles en pacientes con variante conductual de la demencia frontotemporal.
Para acceder al artículo hacé click aquí.
Interoception primes emotional processing: Multimodal evidence from neurodegeneration
Salamone, P., Legaz, A., Sedeño, L., Moguilner, S., Fraile-Vazquez, M., Gonzalez Campo, C., Fittipaldi, S., Yoris, A., Miranda, M., Birba, A., Galiani, A., Abrevaya, S., Neely, A., Martorell Caro, M., Alifano, F., Villagra, R., Anunziata, F., Okada de Oliveira, M., Pautassi, R., Slachevsky, A., Serrano, C., García, A. M. & Ibañez, A. (2021). Interoception primes emotional processing: Multimodal evidence from neurodegeneration. Journal of Neuroscience 41(19), 4276-4292.
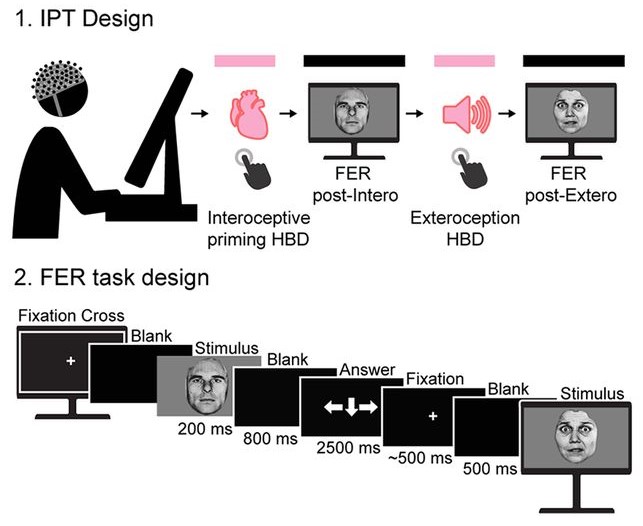
We examined whether and how emotions are primed by interoceptive states combining multimodal measures in healthy controls and neurodegenerative models. In controls, negative emotion recognition and ongoing HEP modulations were increased after interoception. These patterns were selectively disrupted in patients with atrophy across key interoceptive-emotional regions (e.g., the insula and the cingulate in frontotemporal dementia, frontostriatal networks in Parkinson’s disease), whereas persons with Alzheimer’s disease presented generalized emotional processing abnormalities with preserved interoceptive mechanisms. The integration of both domains was associated with the volume and connectivity (salience network) of canonical interoceptive-emotional hubs, critically involving the insula and the anterior cingulate. Our study reveals multimodal markers of interoceptive-emotional priming, laying the groundwork for new agendas in cognitive neuroscience and behavioral neurology.
To access the paper, click here.